Mppt vs. PWM charge controller: Selection of the right option for solar system
Solar energy systems play an important role in meeting the growing energy demands of residential and commercial applications. Selecting the right charge controller is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and efficient use of solar panels.
This article discusses the differences between Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) and pulse width modulation (PWM) charge controllers and helps the reader make an informed decision.
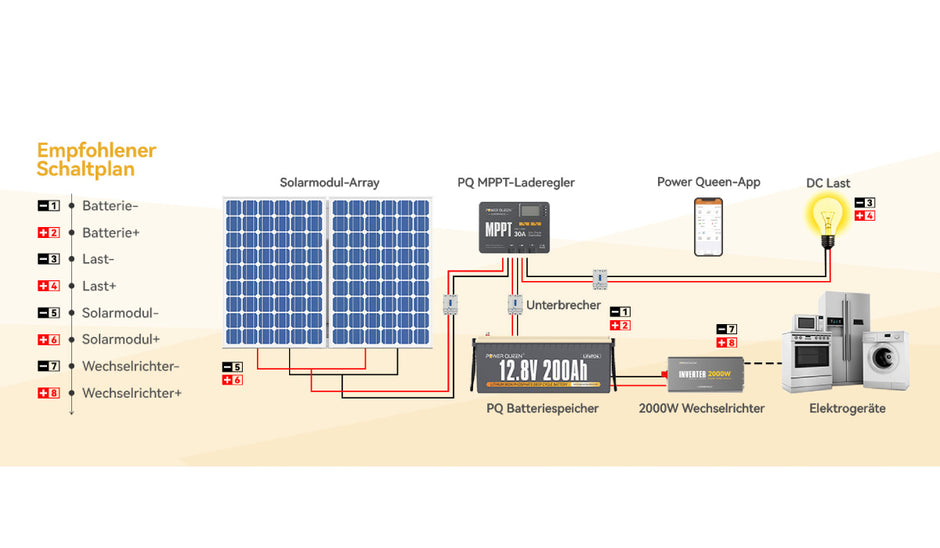
Part 1: Why do you need charge controllers?
To fully understand the importance of charge controllers, it is essential to understand their fundamental necessity in solar power systems.
These systems, consisting of solar panels and batteries, face the challenge of an irregular and fluctuating supply of solar energy. The task of charge controllers is to regulate and optimize the energy flow between the solar panels and the batteries to ensure the batteries receive the correct charge and prevent overcharging or undercharging.
This sophisticated control mechanism not only ensures the longevity and performance of the batteries, but also increases the overall efficiency of the system.
The function of the charge controller

- Protection against reverse switching:Charge controllers typically have a reverse connection protection feature. This means that if the battery is incorrectly connected to the charge controller, it will prevent any current flow, thus protecting both the battery and the charge controller from potential damage.
- Protection against reverse loading:This feature prevents the battery from discharging back into the solar panel array during periods of low or no sunlight. This ensures that the energy generated by the solar panels is efficiently used to charge the battery and not wasted.
- Short circuit protection:Short-circuit protection is designed to prevent damage to the charge controller and other components in the system in the event of a short circuit. It quickly detects excessive current flow and shuts down the circuit to prevent potential damage or hazards.
- Surge protection:Overvoltage protection prevents excessive voltage from damaging the batteries or other components in the system. It monitors voltage levels, and if they exceed a preset limit, the charge controller regulates or interrupts the charging current to protect the battery and the system.
- Overload protection:Overload protection protects the charge controller and the system from excessive power generation. It's especially useful when the solar panel output suddenly increases, for example, because shading has been removed. The charge controller can limit the input power to a level the system can handle.
Overall, these protective features in a charge controller contribute to increasing the safety and reliability of the solar system. They play a crucial role in preventing potential damage to the batteries, charge controller, and other components, ensuring the longevity and efficient operation of the system.
Part 2: Exploring MPPT charge controllers
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) charge controllers are electronic devices used in photovoltaic solar systems to optimize the energy yield of solar modules. They continuously track the maximum power point (MPP) of the solar array and adjust the voltage and current to ensure maximum energy production.
Advantages of MPPT charge controllers
Compared to PWM (pulse-width modulation) charge controllers, MPPT charge controllers are more efficient because they convert the excess voltage from solar panels into additional current, enabling higher power output. By using DC-DC converters, they are capable of converting higher voltages, enabling compatibility with higher-voltage arrays and reducing power loss during the conversion process.

One of the main advantages of MPPT controllers is their ability to to generate more power in poor lighting conditionsThey constantly adjust the operating point of the solar modules to changing environmental conditions, thus ensuring better performance during cloudy or shady periods.
Another advantage of MPPT charge controllers is that they Flexibility in dimensioning the system With PWM controllers, the solar array voltage must match the battery voltage, which can be limiting when designing the system. MPPT controllers, on the other hand, can accept a higher input voltage from the solar modules, allowing more flexibility in sizing and configuring the system.
MPPT charge controllers also offer better scalability of the systemIf you plan to expand your solar system in the future, MPPT charge controllers can accommodate higher voltages in the system and easily handle the increased power.
In summary, compared to PWM controllers, MPPT charge controllers offer higher efficiency, better performance in low-light conditions, compatibility with higher-voltage arrays, flexibility in array sizing, and greater system scalability. However, factors such as budget, system size, and specific application requirements should be considered when deciding between MPPT and PWM controllers. PWM controllers can still be a viable option for smaller systems or those with limited budgets.
Part 3: Exploring PWM charge controllers
PWM (pulse-width modulation) charge controllers are a type of charge controller used in solar systems. They regulate battery charging by rapidly switching the solar panel's output voltage on and off. This creates a square wave with varying pulse widths, allowing the charge controller to gradually reduce the voltage applied to the battery as it reaches its full charge level.
PWM charge controllers have been used in small to medium-sized solar power systems for many years. Compared to MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) controllers, they are simpler and less expensive, making them a more affordable option for certain applications.
However, PWM controllers are less efficient than MPPT controllers. They don't convert excess voltage into additional current, meaning some of the energy from the solar panels goes unused. Furthermore, PWM controllers may struggle to use the power efficiently in low light or cloudy conditions.
Overall, PWM charge controllers are best suited for smaller, lower-voltage solar systems where cost is a major consideration and efficiency is not the highest priority.
Part 4: How do I choose a PWM or MPPT charge controller?
When deciding between PWM and MPPT charge controllers, several key factors should be considered:
- Budget:If you're on a budget or working with a smaller solar system, a PWM charge controller might be a more cost-effective option. They're generally less expensive than MPPT controllers.
- System size:The size of your solar system and its voltage play a crucial role in determining the most suitable charge controller. PWM controllers are ideal for smaller systems with lower voltages, while MPPT controllers are suitable for higher voltages and offer greater scalability.
- Efficiency:If maximizing the efficiency and power output of your solar panels is your top priority, then an MPPT charge controller is the right choice. MPPT controllers are more efficient because they can convert excess voltage into additional current, resulting in higher power output.
- Environmental conditions:Consider the typical weather patterns and environmental conditions at your location. If you frequently experience low light or cloudy conditions, MPPT controllers are better equipped to handle these situations and provide optimal performance.
- Advanced features:MPPT charge controllers often offer advanced features and precise control over charging parameters, such as programmable settings and data monitoring. If these features are important to you, an MPPT controller may be a better choice.

FAQs about the charge controller
1. Can I mix different types of charge controllers in one system?
It is generally not recommended to use different types of charge controllers in a system. Each type has its own operating characteristics, and using different controllers together may result in inefficiencies or compatibility issues.
2.How do I choose a charge controller for my system?
The size of the charge controller should be based on factors such as the maximum voltage and current of the solar panel array and the size of the battery bank. It is recommended to consult the manufacturer's specifications or consult a solar specialist to determine the appropriate size.
3. What types of charge controllers are there?
The two main types of charge controllers are MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). MPPT controllers are more efficient and offer advanced features, while PWM controllers are simpler and more cost-effective.
Conclusion
In summary, compared to PWM controllers, MPPT charge controllers offer higher efficiency, better performance in low-light conditions, compatibility with higher-voltage arrays, flexibility in array sizing, and greater system scalability. However, PWM controllers are simpler and less expensive, making them a suitable option for smaller systems or those on a limited budget.
Remember to consult the manufacturer's instructions and seek professional assistance if you are unsure about installing or using a charge controller in your solar system.
As a one-stop provider of solar system solutions, Power Queen not only LiFePO4 batteries, but also LiFePO4 chargers, portable solar modules, solar charge controllers and much more.
If you have any questions, please contact service.de@ipowerqueen.com, we are always there for you.

























